| Go Back: Module 4: Implicit Bias and Microaggressions | You Are Here: Module 5: Systems of Inequality | Next: Module 6: Indigeneity and Colonialism |
After working through this module, you will be able to:
- List and describe some of the major systems that shape the daily life and life outcomes for people in the United States.
- Describe the ways in which these systems both create and perpetuate societal inequities.
- Analyze how these systems are connected to each other in ways that further compound inequity.
Imagine that you are walking along a lakeshore and see a single dead fish washed up on the shore. You may think that the fish was old, or sick, or that he gave in to the temptation of a fisherman’s hook; in other words, there was something specific to the fish that caused him to end up dead on the shore. Now imagine that a few feet farther along your walk, you see another dead fish, then another, and another – dozens of dead fish washed up on the shore. Would you still think that there’s a problem with the fish, or would you begin to suspect that there might be a problem with the water?
In the United States, we continue to see depressingly predictable statistics related to the life outcomes and living circumstances for people of color and Indigenous people (for an overview of some of these statistics, see Module 1b). Many people in our society look at statistics like this and conclude that we have a “fish problem” – outcomes are worse for these groups because of some deficiency in their own culture, behavior, or biology. In this module, we will instead argue that we have a “lake problem” – outcomes are worse for marginalized groups because the systems and institutions that shape our lives are designed to create and perpetuate inequality along racial lines.
 Explore
Explore
We’ll start this module by completing an activity in our journal. Imagine that you are driving through an unfamiliar city. You notice yourself getting a bit uncomfortable because it seems you have ended up in a “bad neighborhood.” Colloquially, these areas are sometimes called “hoods,” “ghettos,” “slums,” etc. In your journal, draw this neighborhood, and/or write down a list of things you might see there that communicate to you that it’s “bad.”
If you're having trouble with this exercise, click here to see some probing questions that may help you add more details to your neighborhood.
- What stores are present here?
- What are billboards advertising in this neighborhood?
- What are people doing in this neighborhood’s public spaces?
- What kind of vehicles are in this neighborhood?
- What are the options for entertainment and recreation in this neighborhood?
- Where do children spend their time in this neighborhood?
When you're done, click here to see an example drawing. It's OK if your list/drawing is different!
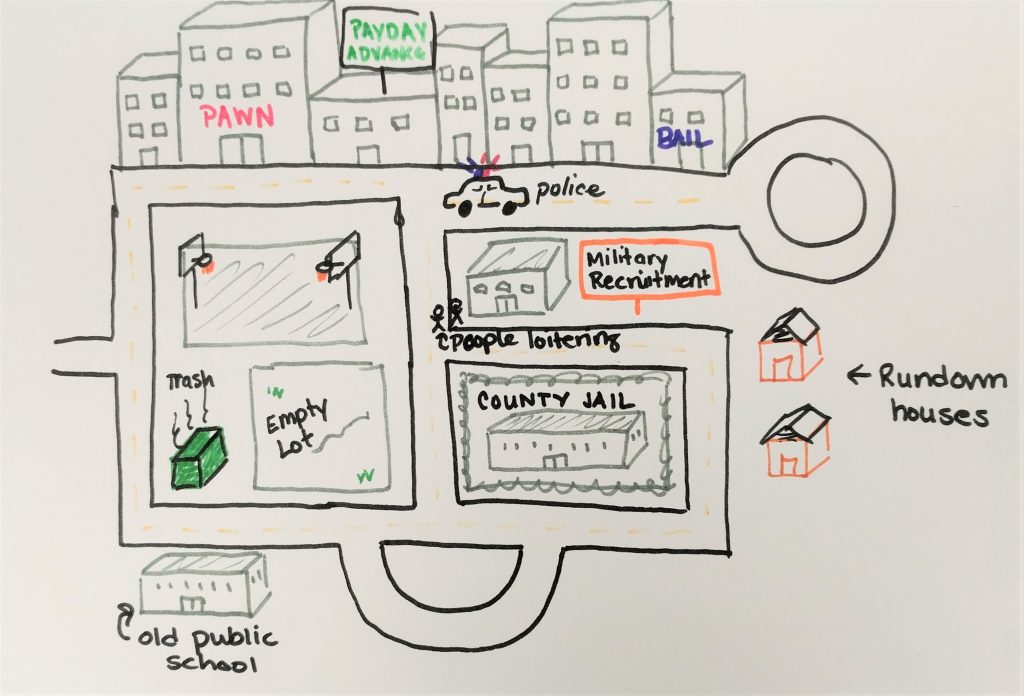
Now, for each of the features of the neighborhood you drew or listed, think about what system it is part of. For example, a jail would be part of the criminal justice system; a school would be part of the education system. Write these systems down in your journal.
When you're done, click here to see what systems we identified for our neighborhood.
- Criminal justice system: jails or prisons, police/police cars, bail offices, law offices
- Educational system: schools
- Food system: Fast food restaurants, convenience stores
- Financial system: Check cashing businesses, payday loan businesses
- Transportation: Buses or other public transportation, older private cars
- Healthcare: Free clinics, urgent care offices
- Housing: Rental units, public / Section 8 housing
- Public services/government: Waste treatment, welfare offices, social services offices, military recruitment centers
- Religion: Churches, religious nonprofits
- Entertainment: strip clubs, internet lottery cafes, basketball courts
- Retail: convenience stores, tobacco shops
On a daily basis, we encounter and interact with dozens of systems (remember, in Module 3, we defined a system as “a set of things that work together for a common purpose or with a common outcome”). When we buy something from a store, we are participating in the retail system. When we pay our taxes, we are interacting with the government as a system. If you are a school librarian or classroom teacher, you are an agent of the educational system. Libraries, too, can be thought of as a system.
On their surfaces, most systems seem to be set up to further the public good. In theory, the educational system exists to prepare everyone to reach their intellectual potential and contribute to society. The police system exists to “protect and serve.” The healthcare system exists to improve everyone’s quality and length of life. Many people do have positive experiences with these systems – experiences that align with the systems’ stated missions. However, not everyone experiences these systems in the same way. When we look at the disparate life outcomes produced by these systems, we can see that systemic rules do not work the same for everyone, and in particular, they do not work well for people of color, people in poverty, and other marginalized people.
To see an example of how this plays out for people of color, let’s examine the criminal justice system in more detail. Inequities in the educational system and in libraries will be explored in detail in Modules 14 and 15.
 Read
Read
The Sentencing Project is a non-profit organization that has worked in the area of criminal justice reform for over 30 years. Read their 2018 report to the United Nations, which shares recent statistics on racial disparities in the U.S. criminal justice system.
Read the NAACP’s Criminal Justice Fact Sheet.
 Watch
Watch
Angela J. Davis is a professor of law at the American University’s Washington College of Law and an expert on racial disparities in the criminal justice system. Watch the short video below, where she gives a big-picture overview of work in this area.
 Explore
Explore
Civil rights lawyer, advocate, and scholar Michelle Alexander wrote a seminal book on inequity in the criminal justice system titled The New Jim Crow. On the book’s website, you can read an excerpt of the book, access some of Alexander’s other writing, listen to a radio documentary series inspired by the text, and find study and organizing guides based on the book. View the book trailer below, then spend some time exploring the resources available at the site linked above.
These findings show that while in theory the criminal justice system is set up to be race-neutral, in practice people of color experience its impacts in very different ways than white people. It is important to note that these disparities are not accidents of the system, nor are they the result of a few actively racist people working within systems. Instead, our systems have been designed to produce these outcomes and will continue to produce inequity unless they are radically reformed. For example, as we learned in Module 2, the criminal justice system was originally designed first as a mechanism to keep enslaved people captive and later to imprison formerly enslaved people as a means of maintaining a cheap labor source. While attitudes toward Black people may have changed since the nineteenth century, the criminal justice system we have now is virtually identical to the system we had then, and it continues to reproduce the same racial inequities.
Many of these inequities result from the fact that the power of these systems, and ownership of them, is concentrated among white and wealthy people. High-poverty communities must interact with these systems every day and in many ways are the communities most affected by our systems and institutions, yet these communities also have the least amount of power to control decision-making within these systems. In other words, there is a power difference between the people controlling the systems and the people impacted by them; this difference in power means that systems have the ability to (and frequently do) oppress marginalized communities.
Who is…
Michelle Alexander

Michelle Alexander is a civil rights lawyer, advocate, and legal scholar. She has experience as a litigator and as a law school professor. She also served as the director of the Racial Justice Project for the ACLU of Northern California.
To learn more about Michelle Alexander and her work:
- Watch a panel discussion on mass incarceration from the 2018 Peace and Justice Summit featuring Alexander, Sherrilyn Ifill, and Jelani Cobb.
- Visit the About the Author, Other Writings, and Speeches pages of The New Jim Crow website.
For nearly every system currently operating in the United States, there are people or organizations keeping track of disparities within it. The resources listed below are starting points for exploring the inequities reproduced by some of the major systems in our society.
- Healthcare system: Medline Plus resource guide for health disparities; National Healthcare Quality and Disparities Reports
- Food system: Feeding America – Who Goes Hungry?; America’s growing food inequality problem (Washington Post)
- Transportation system: Back of the Bus – Mass transit, race, and inequality (WNYC); America’s Unfair Rules of the Road (Slate); What city bus systems can tell us about race, poverty, and us (Washington Post)
- Housing system: Time for justice: Tackling race inequalities in health and housing (Brookings); How housing intensifies the racial wealth gap (Citylab)
- Financial system: Discriminatory effects of credit scoring on communities of color [PDF] (Suffolk Law Review)
- Government: How privatization increases inequality [PDF] (In the Public Interest)
Interconnected Systems
Now that we have spent some time thinking about how individual systems oppress, marginalize, and discriminate against people of color, let’s explore how these systems interact with each other.
No system operates completely independently of other systems. Thus, discrimination and inequity in one system often carry over to other areas, creating mutually reinforcing structures of oppression (we will explore this idea further in the intersectionality module). Click through the slideshow below to see some examples of how the criminal justice system is related to five other major systems.
See the notes section of each slide by pressing the settings (gear) button for sources and image credits.
 Reflect
Reflect
In your journal, make more connections among the six systems depicted. Can you think of at least one way that each listed system is connected to each other listed system? If you get stuck, you may find it helpful to search online.
When you have made all of the connections you can, think about this question and write down your thoughts in the journal: What does the interconnectedness of systems of oppression mean for anti-racist work in the United States?
Then, click here to view a Padlet where you can share your examples and/or question responses and see what others have come up with.What does this mean?
It can be tempting to react with despair when confronting the realities of systemic oppression. Individual people who work within various systems typically play only a small role in the overall functioning of their system and have little or no capacity to change the way their system functions on a large scale. Even the people “in charge” of a system often lack real transformative power, because their positional power is dependent on the continuation of the system they lead. In addition, it is extremely difficult for someone who wants to radically change the status quo to reach the upper echelons of power within a system in the first place.
However, this does not mean that individuals have no power at all. Most of us can be thought of as gatekeepers: someone in an organizational or institutional role who can make decisions about who gets access to our organization’s services and resources. For example, a librarian has some control over who is permitted in the library and when, which books and other resources people can access (especially through the collection development process), which programs to offer, and which community partners to work with. These are not meaningless decisions, even if they do not change the overall functioning of the library system.
In addition, there are many individuals and organizations advocating for large-scale reform of major institutions and systems within the United States. For example, in the area of criminal justice reform, the Southern Poverty Law Center is working through litigation and advocacy to end mass incarceration, and activist Mariame Kaba has a long history of criminal justice reform work including Project NIA, a grassroots organization with a vision to end youth incarceration. Similar efforts are underway for other major systems. Getting involved with some of these efforts is possible no matter what your current occupation or location.
 Reflect
Reflect
In your journal, reflect on these questions: How could multiple systems be affecting the youth you work with at your library? What can you do at an individual level, library level, and systems level to change the way BIYOC and their families are impacted? What are you doing about the ways racism exists in your library?
 But Wait!
But Wait!
In this section, we address common questions and concerns related to the material presented in each module. You may have these questions yourself, or someone you’re sharing this information with might raise them. We recommend that for each question below, you spend a few minutes thinking about your own response before clicking the arrow to the left of the question to see our response.
There are lots of great people working within these systems. Isn't it unfair to say that the systems as a whole are unjust?Why haven't I heard about reform efforts in some of these systems?
Isn't it unrealistic to imagine completely transformed systems? Shouldn't we set more reasonable goals for incremental change?
| Go Back: Module 4: Implicit Bias and Microaggressions | You Are Here: Module 5: Systems of Inequality | Next: Module 6: Indigeneity and Colonialism |
